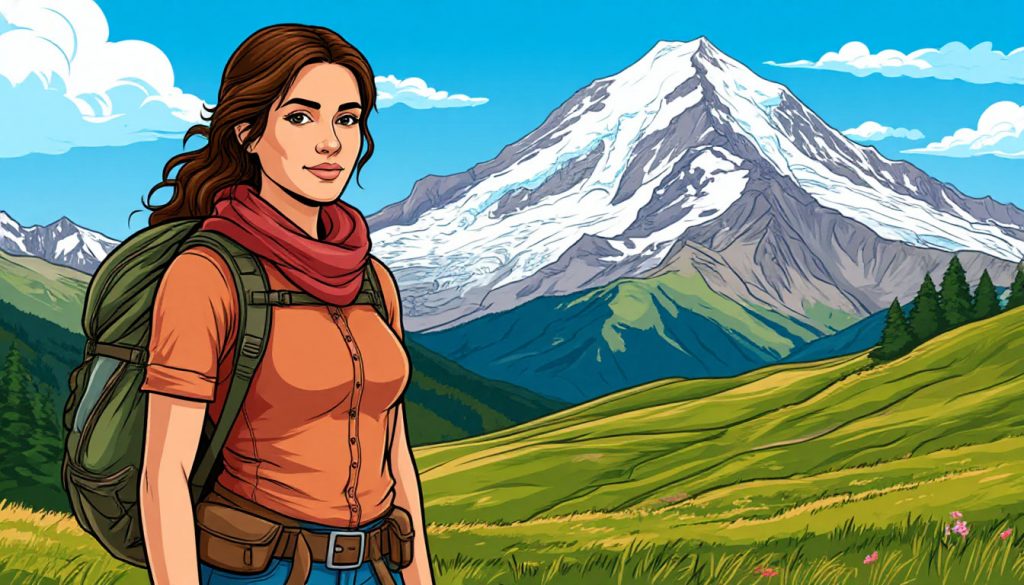
Mount Elbrus is a dormant stratovolcano located in the western Caucasus Mountains of southern Russia, near the border with Georgia. At an elevation of 5,642 meters (18,510 feet) above sea level, it is officially recognized as the highest mountain in Europe and one of the famous Seven Summits — the tallest peaks on each continent.
Despite being a volcano, Elbrus hasn’t erupted in recorded history, making it dormant but not extinct.
Geological Origins and Structure
Elbrus is actually a double-coned volcano, with two main summits:
- Western summit: 5,642 m (higher)
- Eastern summit: 5,621 m
The mountain formed approximately 2.5 million years ago as part of the Alpine orogeny, a mountain-building event that also created the Alps and other ranges. Although the last known eruption occurred over 2,000 years ago, the presence of fumaroles (gas vents) and glacial heat anomalies suggests ongoing subterranean activity.
Elbrus is also covered by 22 glaciers, which feed into rivers supplying the surrounding regions.
Climbing Mount Elbrus
Elbrus is considered a technical but accessible climb for experienced hikers. Most ascents are done from the south side, where a cable car and mountain huts make logistics easier.
Challenges for climbers include:
- Severe cold and rapidly changing weather
- Altitude sickness due to thin air
- Crevasses and snow-covered slopes
Despite these risks, Elbrus is climbed by thousands each year and is often seen as an entry point for mountaineers attempting the Seven Summits.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Elbrus has held symbolic meaning for centuries, featuring in ancient Greek, Georgian, and Turkic mythology. It is sometimes associated with the legend of Prometheus, who was chained to a mountain for stealing fire from the gods.
During World War II, the mountain was briefly occupied by Nazi troops, and the Soviet army famously raised their flag on the summit to reclaim it.
Today, Elbrus is a national symbol and a popular destination for both tourism and sport.
Environmental Importance
The mountain’s glaciers are essential for local water supply, and its ecosystem supports:
- Alpine meadows with rare plants
- Mountain goats, snow leopards, and other wildlife
- Endemic species found only in the Caucasus region
However, climate change poses a risk to its glaciers, which are receding at increasing rates.
Glossary
- Stratovolcano – A large, steep volcano built from layers of lava and ash.
- Dormant volcano – A volcano that has not erupted recently but could erupt again.
- Fumarole – An opening in the ground that emits steam and volcanic gases.
- Glacier – A slow-moving mass of ice formed by compacted snow.
- Seven Summits – The highest mountain on each of the seven continents.