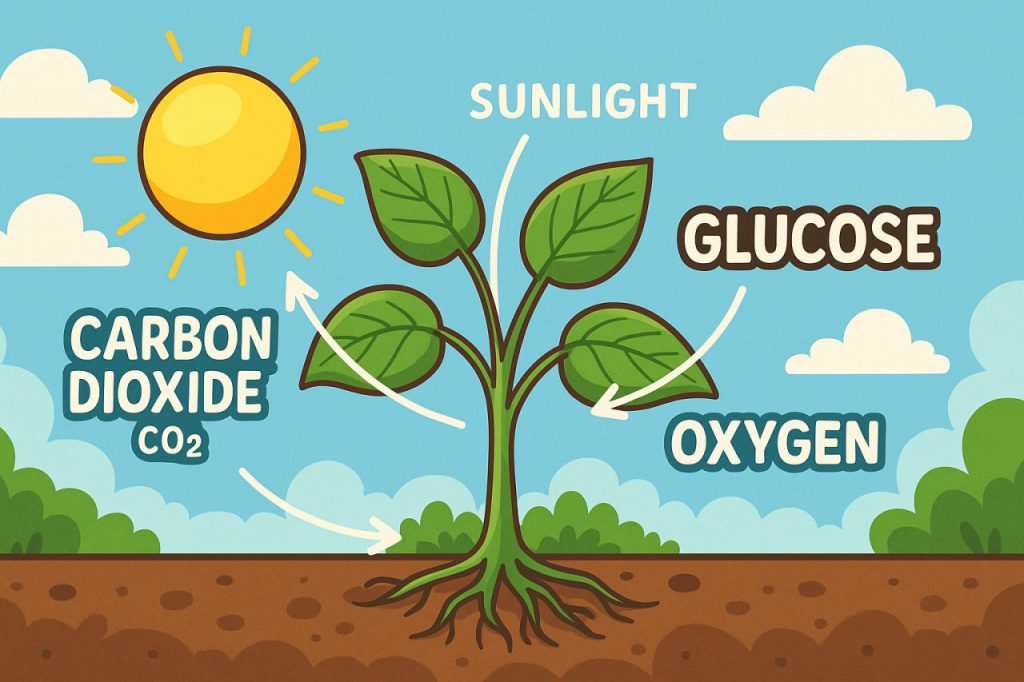
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen. It is one of the most important biological processes on Earth, supporting nearly all life by creating the oxygen we breathe and the energy that fuels ecosystems.
Without photosynthesis, there would be no green plants, no animals that depend on plants, and no breathable atmosphere.
How Photosynthesis Works
Photosynthesis happens mainly in the leaves of green plants, inside tiny structures called chloroplasts. These contain a green pigment known as chlorophyll, which captures light energy.
The basic formula for photosynthesis is:
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) + Water (H₂O) + Sunlight → Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) + Oxygen (O₂)
This reaction happens in two main stages:
- Light-dependent reactions – sunlight splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the air.
- Calvin cycle – the plant uses the hydrogen and carbon dioxide to make glucose, which stores energy for the plant.
Why Photosynthesis Is So Important
- Produces oxygen: More than 70% of the oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere comes from marine photosynthesis (mainly algae).
- Provides food: Plants make glucose, which they use for energy and growth. Animals, including humans, get energy by eating plants or plant-eating animals.
- Regulates climate: By absorbing carbon dioxide, photosynthesis helps reduce the greenhouse effect and cool the planet.
Photosynthesis in Agriculture and the Environment
Modern farming relies on understanding photosynthesis to maximize crop yields. Greenhouses use artificial lighting to boost the process when natural light is limited. Forests and oceans act as natural “carbon sinks,” storing CO₂ and helping slow climate change.
Protecting these natural systems is essential to preserving the photosynthetic balance of the planet.
Glossary
- Photosynthesis – The process by which plants use sunlight to make food and oxygen.
- Chlorophyll – The green pigment in plants that absorbs sunlight.
- Glucose – A simple sugar that stores energy for plants.
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) – A gas absorbed from the air by plants during photosynthesis.
- Chloroplast – A plant cell structure where photosynthesis takes place.