An ecosystem is a dynamic community of living organisms interacting with one another and with their physical environment. From vast rainforests to tiny ponds, ecosystems are the foundation of life on Earth. They provide food, clean air, water, and shelter to countless species—including humans.
What Makes Up an Ecosystem?
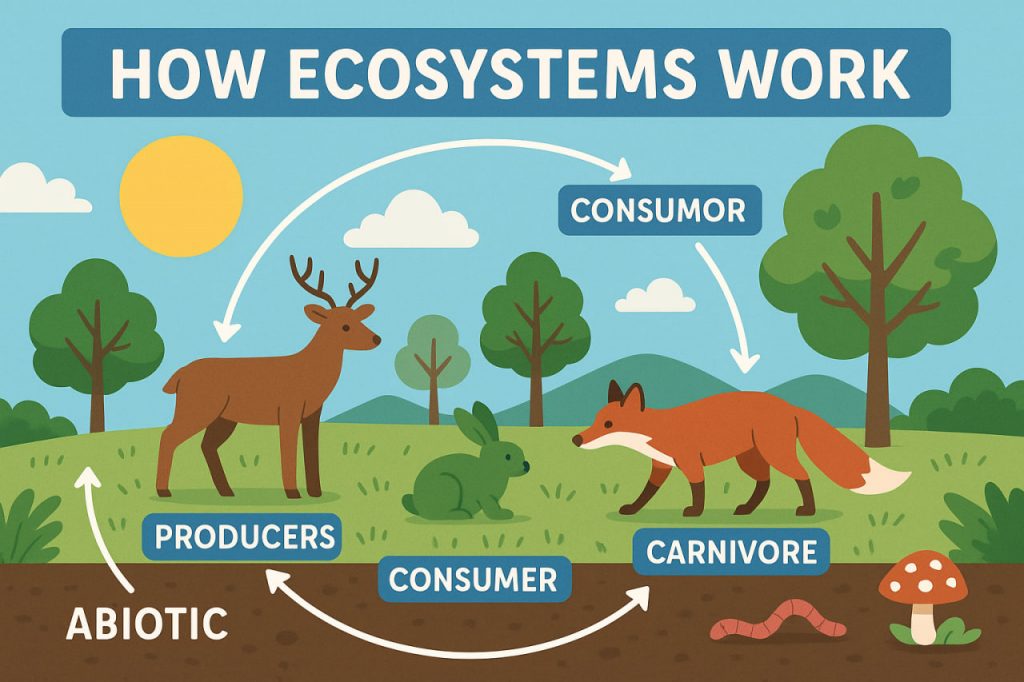
Every ecosystem includes biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components working together:
Biotic (living):
- Producers: Plants and algae that make energy through photosynthesis
- Consumers: Animals that eat plants or other animals
- Decomposers: Fungi and bacteria that break down dead matter
Abiotic (non-living):
- Sunlight
- Water
- Soil
- Temperature
- Minerals and gases
These elements interact constantly to keep the ecosystem balanced.
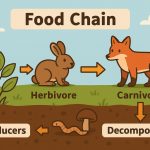
Trophic Levels: The Food Chain
Ecosystems are powered by energy flow, starting from the Sun:
- Producers (plants) convert sunlight into energy
- Primary consumers (herbivores) eat the plants
- Secondary consumers (carnivores) eat herbivores
- Tertiary consumers (top predators) eat other animals
- Decomposers recycle nutrients by breaking down waste and dead organisms
This system creates food chains and food webs that link all species.
Types of Ecosystems
Ecosystems vary depending on location and climate. Major types include:
- Terrestrial: Forests, grasslands, deserts, tundras
- Aquatic: Freshwater (lakes, rivers) and marine (oceans, coral reefs)
- Urban: Cities with modified ecosystems but still supporting life
- Micro-ecosystems: Like a rotting log or tidepool
Each type supports unique biodiversity and ecological processes.
Ecosystem Services
Ecosystems provide vital benefits known as ecosystem services:
- Provisioning: Food, water, timber, medicine
- Regulating: Air quality, climate, disease control
- Supporting: Nutrient cycles, soil formation, pollination
- Cultural: Recreation, spiritual value, education
Healthy ecosystems are essential for human survival.
Threats to Ecosystems
Human activity is putting many ecosystems under stress:
- Deforestation
- Pollution
- Climate change
- Overfishing and habitat destruction
- Invasive species
When ecosystems become unbalanced, species decline, and essential services are lost.
How to Protect Ecosystems
- Conserve natural habitats
- Reduce waste and pollution
- Support sustainable farming and fishing
- Plant native species
- Protect endangered animals and plants
Even small actions—like using less plastic or planting trees—help preserve ecosystems.
Conclusion
Ecosystems are complex networks that keep our planet alive. Understanding how they work reminds us that all life is interconnected. Protecting ecosystems means protecting the Earth—and ourselves.
Glossary
- Ecosystem: A community of living things and their environment
- Biodiversity: The variety of life in an ecosystem
- Producer: An organism that makes its own food through photosynthesis
- Consumer: An organism that eats others for energy
- Decomposer: Organisms that break down dead material into nutrients