Insects may be small, but they are among the most important creatures on Earth. With over 5 million estimated species, insects play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. They pollinate plants, decompose organic matter, control pests, and serve as food for countless other animals.
Key Ecological Roles of Insects
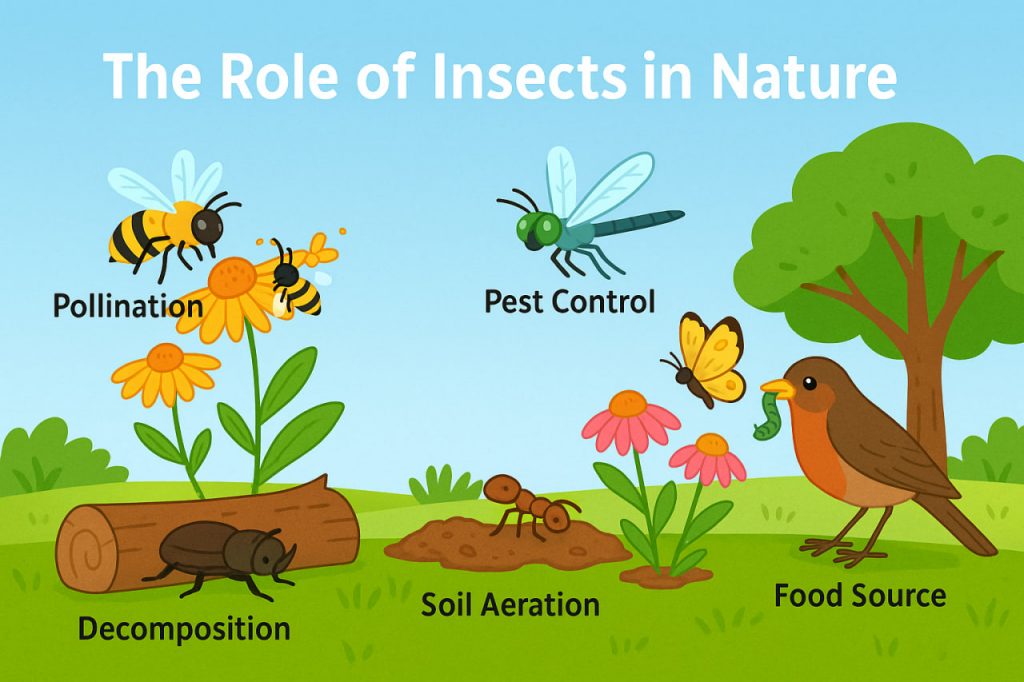
1. Pollination
Many flowering plants—including fruits and vegetables—depend on insect pollinators to reproduce.
- Bees, butterflies, beetles, and flies transfer pollen from one flower to another
- Around 75% of global food crops benefit from pollination
- Without them, food production and wild plant diversity would collapse
2. Decomposition
Insects like beetles, flies, and ants help break down dead animals, plants, and waste.
- They return vital nutrients to the soil
- Support healthy plant growth
- Reduce disease by clearing organic debris
3. Pest Control
Predatory insects and parasitoids naturally manage populations of harmful species.
- Ladybugs eat aphids
- Dragonflies consume mosquitoes
- Wasps lay eggs in caterpillars, keeping pest numbers in check
This reduces the need for chemical pesticides and supports sustainable agriculture.
4. Soil Aeration and Enrichment
Burrowing insects like ants and beetles:
- Loosen and mix soil
- Improve water absorption and root growth
- Distribute organic material through tunnels
Healthy soil leads to more productive ecosystems.
5. Food Source for Other Animals
Insects are a foundation of many food chains:
- Birds, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals rely on them
- Aquatic insects feed fish and other freshwater life
- Humans also consume insects in many cultures due to their high protein content
Insects and Biodiversity
Insects support the biodiversity of entire ecosystems:
- Their interactions with plants, fungi, and other animals create stable communities
- Losing insect populations causes cascading effects through the food web
- Many endangered species rely on specific insects for survival
Threats to Insects
Insect populations are declining globally due to:
- Habitat loss and deforestation
- Pesticide use and pollution
- Climate change
- Invasive species
This threatens crop pollination, food webs, and soil fertility.
How to Help Insects
- Plant native flowers and reduce lawn space
- Avoid pesticides and use organic methods
- Create habitats with logs, rocks, and water sources
- Support conservation and sustainable farming
- Share important information with each other
Conclusion
Insects are more than just bugs—they are essential engineers of the natural world. Their work behind the scenes sustains ecosystems, food systems, and biodiversity.
Glossary
- Pollination: Transfer of pollen for plant reproduction
- Decomposer: Organism that breaks down dead material
- Parasitoid: An insect that lays eggs in or on another insect
- Biodiversity: The variety of life in a given area
- Food web: A system of interconnected food chains