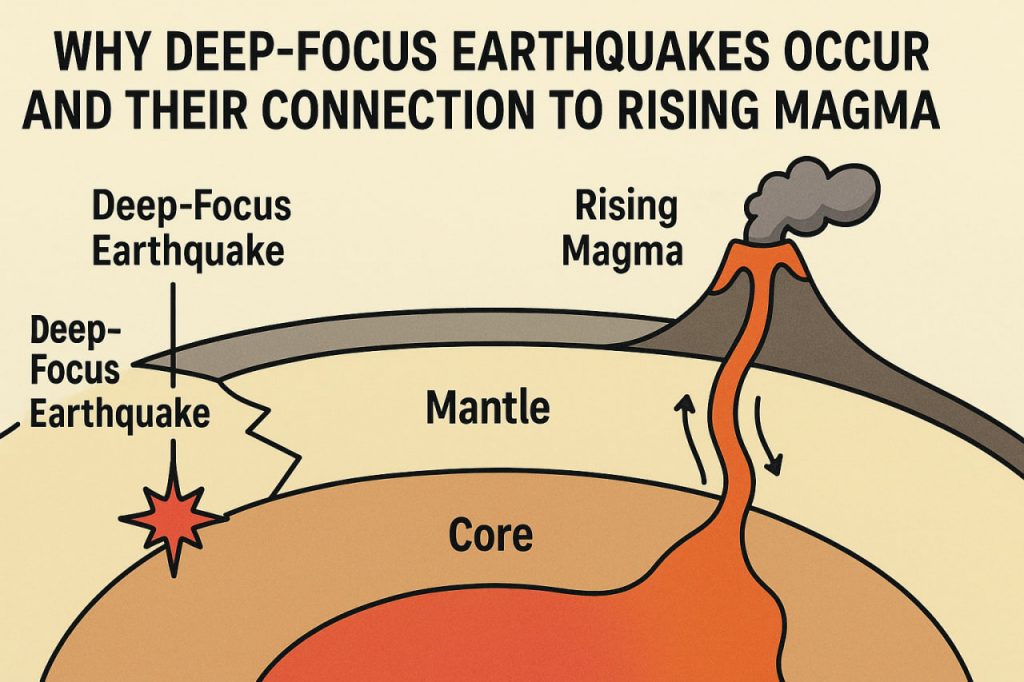
Deep-focus earthquakes are seismic events that occur at depths greater than 300 km below Earth’s surface, sometimes reaching 700 km. Unlike shallow earthquakes, which are linked to surface faults and tectonic movements, deep-focus earthquakes happen far within the mantle, where conditions are extreme, and rock behaves differently.
Causes of Deep-Focus Earthquakes
The primary cause of deep-focus earthquakes is the subduction of tectonic plates. When one plate sinks beneath another into the mantle, it carries cold, rigid lithosphere deep inside Earth. These slabs maintain their rigidity under enormous pressure, allowing stress to build up. Eventually, sudden ruptures or phase transitions within the slab release seismic energy, creating deep earthquakes.
Role of Mineral Phase Changes
At great depths, high pressures and temperatures cause minerals inside subducted slabs to change their crystal structure. For example, olivine, a major mantle mineral, can suddenly transform into denser forms like spinel. These abrupt changes release energy and contribute to deep-focus earthquakes, explaining why they occur in zones where slabs penetrate deeply.
Is Magma Involved in Deep-Focus Earthquakes?
Magma activity is usually associated with shallow to intermediate earthquakes near volcanoes. At depths of hundreds of kilometers, rocks are too rigid and temperatures are too high for magma pockets to form in the same way. Instead, the earthquakes come from mechanical stress within subducting slabs. However, this is a theoretical concept, and some scientists argue otherwise.
Differences from Shallow Earthquakes
Shallow earthquakes are driven by brittle fracture and movement along faults near the surface, often linked to volcanic activity or tectonic boundaries. Deep-focus earthquakes, however, occur in environments where rock should normally deform plastically. This paradox makes them unique, and they are still an area of active research in seismology.
Scientific Importance
Studying deep-focus earthquakes helps scientists understand the structure of Earth’s interior, the behavior of subducting slabs, and mantle dynamics. They provide evidence of how materials transform under extreme conditions, offering insights into the planet’s long-term geological evolution.
Conclusion
Deep-focus earthquakes are caused primarily by subducted slabs and mineral transformations deep within Earth’s mantle. They remain one of the most fascinating puzzles of seismology, showing how powerful geological processes continue far beneath our feet.
Glossary
- Deep-focus earthquake – seismic event occurring at depths greater than 300 km.
- Subduction – process where one tectonic plate sinks beneath another.
- Lithosphere – Earth’s rigid outer layer, including crust and upper mantle.
- Olivine – common mantle mineral that undergoes phase changes under pressure.
- Phase transition – transformation of a mineral into a denser form under high pressure.
- Mantle – thick layer of Earth between the crust and core.