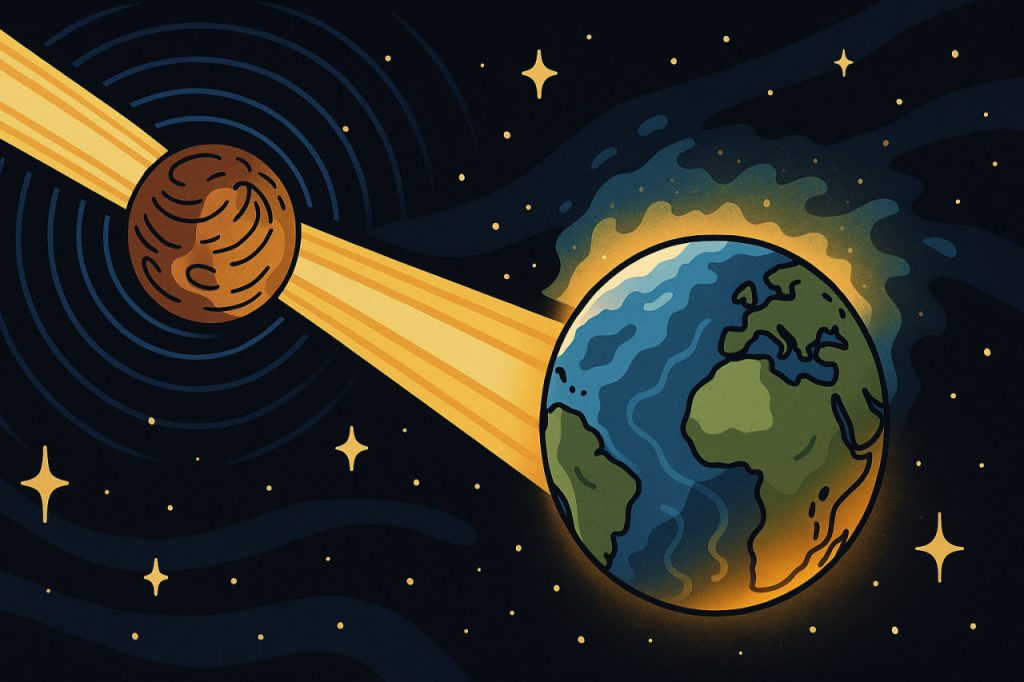
A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star, the dense remnant of a massive star after a supernova. Pulsars emit powerful beams of electromagnetic radiation, including radio waves, X-rays, and gamma rays, which sweep through space like cosmic lighthouses.
Intensity of Pulsar Radiation
The radiation from pulsars is billions of times more intense than the Sun’s output. If Earth were close to a pulsar, the flux of high-energy particles and gamma rays would overwhelm the atmosphere, stripping away its protective layers and exposing the surface to lethal radiation.
Effects on Earth’s Atmosphere
A nearby pulsar would ionize and gradually erode Earth’s atmosphere. The ozone layer would be destroyed, leaving the planet vulnerable to harmful ultraviolet radiation. Without atmospheric protection, life as we know it could not survive on the surface.
Impact on Life
Radiation from a pulsar would cause mass extinctions within a very short period. DNA and cellular structures would be irreparably damaged, and ecosystems would collapse. Only underground or deep-sea organisms might survive temporarily, shielded by rock or water.
Gravitational Influence
Besides radiation, a pulsar’s gravity is extremely intense due to its compact mass. If Earth were to pass too close, tidal forces could disrupt its orbit, deform the planet, or even tear it apart.
Observational Perspective
Astronomers study pulsars from a safe distance using radio telescopes. These objects serve as natural laboratories for testing the laws of physics under extreme conditions. While their destructive power is immense, they are far away from Earth — the nearest known pulsar is hundreds of light-years distant.
Conclusion
If Earth fell under the influence of a pulsar, the combination of lethal radiation, atmospheric destruction, and gravitational forces would make survival impossible. Fortunately, pulsars are distant cosmic objects, and their danger remains theoretical for our planet.
Glossary
- Pulsar – rapidly rotating neutron star emitting beams of radiation.
- Neutron star – dense stellar remnant formed after a supernova explosion.
- Radiation – energy emitted as waves or particles, harmful in high doses.
- Ionization – process where atoms lose electrons due to high-energy radiation.
- Tidal forces – gravitational stretching caused by massive objects.
- Supernova – stellar explosion that creates neutron stars and pulsars.